Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you:
Create an Auth0 Application
Go to your
Auth0 Dashboard to create a new Auth0 Application.
- Navigate to Applications > Applications in the left sidebar.
- Click the Create Application button in the top right.
- In the pop-up select Regular Web Applications and click Create.
- Once the Application is created, switch to the Settings tab.
- Scroll down to the Application URIs section.
- Set Allowed Callback URLs as:
http://localhost:3000/auth/callback - Set Allowed Logout URLs as:
http://localhost:3000 - Click Save in the bottom right to save your changes.
To learn more about Auth0 applications, read
Applications.
Create an Auth0 FGA account
Prepare Next.js app
Recommended: To use a starter template, clone the Auth0 AI samples repository:git clone https://github.com/auth0-samples/auth0-ai-samples.git
cd auth0-ai-samples/authenticate-users/langchain-next-js
Install dependencies
In the root directory of your project, install the following dependencies:
@auth0/ai-langchain: Auth0 AI SDK for LangChain built for GenAI applications powered by LangChain.@langchain/langgraph: For building stateful, multi-actor applications with LLMs.langchain: The LangChain library.@langchain/core: Core LangChain dependencies.@langchain/openai: OpenAI provider for LangChain.zod: TypeScript-first schema validation library.langgraph-nextjs-api-passthrough: API passthrough for LangGraph.
npm install @auth0/ai-langchain@3 @langchain/core@0.3 @langchain/langgraph@0.3 @langchain/openai@0.6 langchain@0.3 langgraph-nextjs-api-passthrough@0.1
Update the environment file
Copy the .env.example file to .env.local and update the variables with your Auth0 credentials. You can find your Auth0 domain, client ID, and client secret in the application you created in the Auth0 Dashboard.Set up an FGA Store
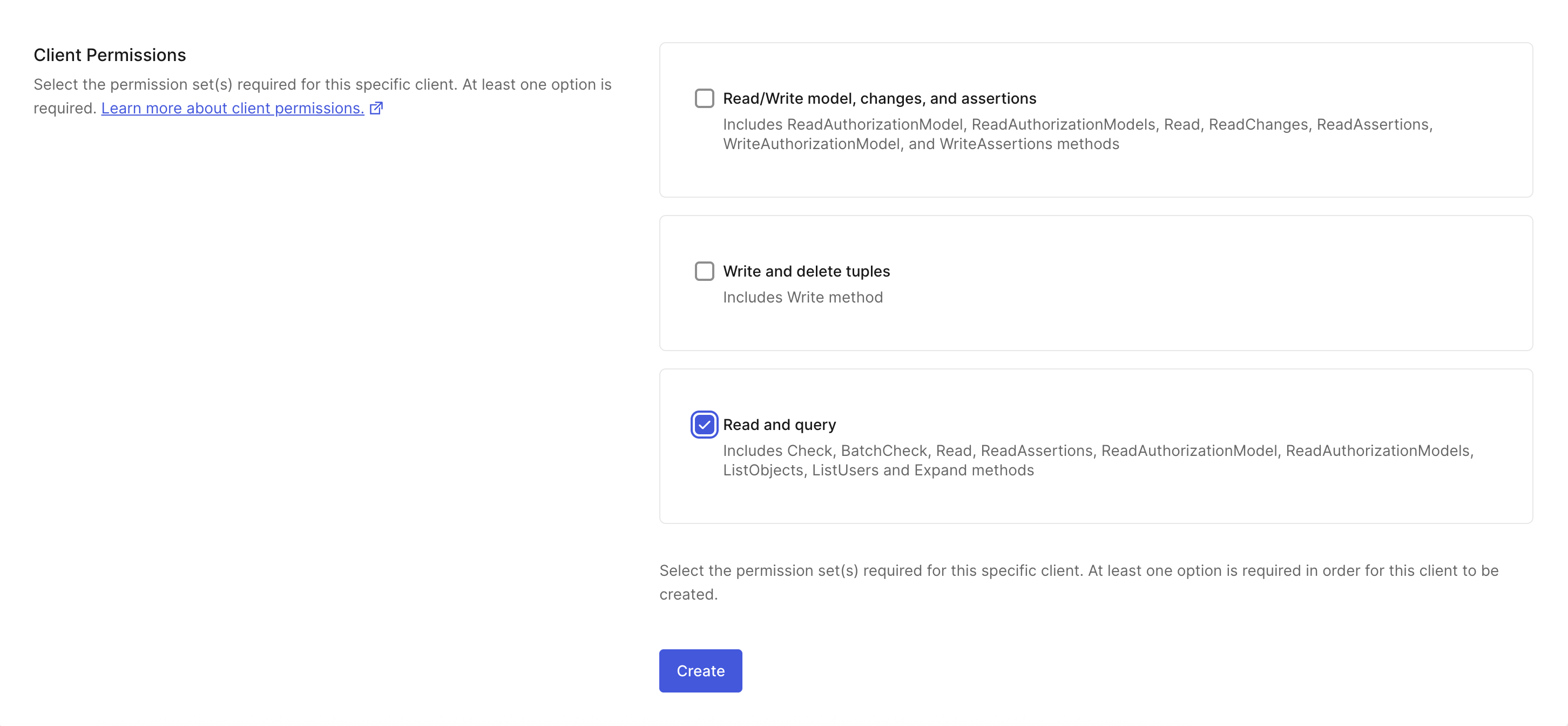
In the Auth0 FGA dashboard:Navigate to Settings. In the Authorized Clients section, click +
Create Client.
Give your client a name and mark all the client permissions that are
required for your use case. For the quickstart, you’ll only need Read and
query.
.env.local file with the following content to the root directory of the project. Click Continue to see the FGA_API_URL and FGA_API_AUDIENCE.The confirmation dialog will provide you with all the information that you need for your environment file.# You can use any provider of your choice supported by Vercel AI
OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
# Auth0 FGA
FGA_STORE_ID=<your-fga-store-id>
FGA_CLIENT_ID=<your-fga-store-client-id>
FGA_CLIENT_SECRET=<your-fga-store-client-secret>
FGA_API_URL=https://api.xxx.fga.dev
FGA_API_AUDIENCE=https://api.xxx.fga.dev/
model
schema 1.1
type user
type doc
relations
define owner: [user]
define viewer: [user, user:*]
- You can upload documents through the UI (
src/app/documents/page.tsx).
- Uploaded documents are processed by the API route (
src/app/api/documents/upload/route.ts).
- APIs for uploading and retrieving documents are defined in (
src/lib/actions/documents.ts).
- Database is defined in
src/lib/db.
- FGA helpers are defined in
src/lib/fga.
- Documents are stored as embeddings in a vector database for efficient retrieval (
src/lib/rag/embedding.ts).
Access Control with Auth0 FGA
- When a document is uploaded, the app automatically creates FGA tuples to define which users can access which documents. A tuple signifies a user’s relation to a given object. For example, the below tuple implies that all users can view the
<document name> object.
- Navigate to the Tuple Management section to see the tuples being added. If you want to add a tuple manually for a document, click + Add Tuple. Fill in the following information:
- User:
user:*
- Object: select doc and add
<document name> in the ID field
- Relation:
viewer
Define a RAG tool that uses the FGAFilter to filter authorized data from the vector database:src/lib/tools/context-docs.ts
import { tool } from "@langchain/core/tools";
import { z } from "zod";
import { FGARetriever } from "@auth0/ai-langchain/RAG";
import { getVectorStore } from "@/lib/rag/embedding";
export const getContextDocumentsTool = tool(
async ({ question }, config) => {
const user = config?.configurable?._credentials?.user;
if (!user) {
return "There is no user logged in.";
}
const vectorStore = await getVectorStore();
if (!vectorStore) {
return "There is no vector store.";
}
const retriever = FGARetriever.create({
retriever: vectorStore.asRetriever(),
buildQuery: (doc) => ({
user: `user:${user?.email}`,
object: `doc:${doc.metadata.documentId}`,
relation: "can_view",
}),
});
// filter docs based on FGA authorization
const documents = await retriever.invoke(question);
return documents.map((doc) => doc.pageContent).join("\n\n");
},
{
name: "get_context_documents",
description:
"Use the tool when user asks for documents or projects or anything that is stored in the knowledge base.",
schema: z.object({
question: z.string().describe("the users question"),
}),
}
);
/src/app/api/chat/[..._path]/route.ts file with the following code to pass the user credentials to your agent:src/app/api/chat/[..._path]/route.ts
import { initApiPassthrough } from "langgraph-nextjs-api-passthrough";
import { getUser } from "@/lib/auth0";
export const { GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, runtime } =
initApiPassthrough({
apiUrl: process.env.LANGGRAPH_API_URL,
baseRoute: "chat/",
bodyParameters: async (req, body) => {
if (
req.nextUrl.pathname.endsWith("/runs/stream") &&
req.method === "POST"
) {
return {
...body,
config: {
configurable: {
_credentials: {
user: await getUser(),
},
},
},
};
}
return body;
},
});
src/lib/auth0.ts://... existing code
export const getUser = async () => {
const session = await auth0.getSession();
return session?.user;
};
/src/lib/agent.ts file with the following code to add the tool to your agent:import { getContextDocumentsTool } from "./tools/context-docs";
//... existing code
const tools = [
//... existing tools
getContextDocumentsTool,
];
//... existing code
Test your application
Start the database and create required tables:# start the postgres database
docker compose up -d
# create the database schema
npm run db:migrate
npm run all:dev. Then, navigate to http://localhost:3000.This will open the LangGraph Studio in a new tab. You can close it as we won’t
require it for testing the application.
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you:
Create an Auth0 Application
Go to your
Auth0 Dashboard to create a new Auth0 Application.
- Navigate to Applications > Applications in the left sidebar.
- Click the Create Application button in the top right.
- In the pop-up select Regular Web Applications and click Create.
- Once the Application is created, switch to the Settings tab.
- Scroll down to the Application URIs section.
- Set Allowed Callback URLs as:
http://localhost:8000/api/auth/callback - Set Allowed Logout URLs as:
http://localhost:5173 - Click Save in the bottom right to save your changes.
To learn more about Auth0 applications, read
Applications.
Create an Auth0 FGA account
Prepare the FastAPI app
Recommended: Use the starter template by cloning the Auth0 AI samples repository:git clone https://github.com/auth0-samples/auth0-ai-samples.git
cd auth0-ai-samples/authenticate-users/langchain-fastapi-py
backend/: contains the backend code for the Web app and API written in Python using FastAPI and the LangGraph agent.frontend/: contains the frontend code for the Web app written in React as a Vite SPA.
Install dependencies
In the backend directory of your project, install the following dependencies:
auth0-ai-langchain: Auth0 AI SDK for LangChain built for GenAI applications powered by LangChain.langgraph: LangGraph for building stateful, multi-actor applications with LLMs.langchain-openai: OpenAI provider for LangChain.langgraph-cli: LangGraph CLI for running a local LangGraph server.openfga-sdk: OpenFGA SDK for Fine-Grained Authorization.
Make sure you have uv installed and run the following command to install the dependencies:cd backend
uv sync
uv add "auth0-ai-langchain>=1.0.0b3" openfga-sdk langgraph langchain-openai "langgraph-cli[inmem]" --prerelease=allow
Update the environment file
Copy the .env.example file to .env and update the variables with your Auth0 credentials. You can find your Auth0 domain, client ID, and client secret in the application you created in the Auth0 Dashboard.Set up an FGA Store
In the Auth0 FGA dashboard:Navigate to Settings. In the Authorized Clients section, click +
Create Client.
Give your client a name and mark all the client permissions that are
required for your use case. For the quickstart, you’ll only need Read and
query.
.env.local file with the following content to the root directory of the project. Click Continue to see the FGA_API_URL and FGA_API_AUDIENCE.The confirmation dialog will provide you with all the information that you need for your environment file.# You can use any provider of your choice supported by Vercel AI
OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
# Auth0 FGA
FGA_STORE_ID=<your-fga-store-id>
FGA_CLIENT_ID=<your-fga-store-client-id>
FGA_CLIENT_SECRET=<your-fga-store-client-secret>
FGA_API_URL=https://api.xxx.fga.dev
FGA_API_AUDIENCE=https://api.xxx.fga.dev/
model
schema 1.1
type user
type doc
relations
define owner: [user]
define viewer: [user, user:*]
- You can upload documents through the API endpoints (
backend/app/api/routes/documents.py).
- Uploaded documents are processed and stored with embeddings for efficient retrieval.
- APIs for uploading and retrieving documents are defined in the application routes.
- Database models are defined in
backend/app/models.
- FGA helpers are implemented in
backend/app/core/fga.py.
- Documents are stored as embeddings in a PostgreSQL vector database (
backend/app/core/rag.py).
Access Control with Auth0 FGA
- When a document is uploaded, the app automatically creates FGA tuples to define which users can access which documents. A tuple signifies a user’s relation to a given object. For example, the below tuple implies that all users can view the
<document name> object.
- Navigate to the Tuple Management section to see the tuples being added. If you want to manually add a tuple for a document, click + Add Tuple. Fill in the following information:
- User:
user:*
- Object: select doc and add
<document name> in the ID field
- Relation:
viewer
Define a RAG tool that uses the FGARetriever to filter authorized data from the vector database:backend/app/agents/tools/context_docs.py
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfig
from langchain_core.tools import StructuredTool
from auth0_ai_langchain import FGARetriever
from openfga_sdk.client.models import ClientBatchCheckItem
from pydantic import BaseModel
from app.core.rag import get_vector_store
class GetContextDocsSchema(BaseModel):
question: str
async def get_context_docs_fn(question: str, config: RunnableConfig):
"""Use the tool when user asks for documents or projects or anything that is stored in the knowledge base"""
if "configurable" not in config or "_credentials" not in config["configurable"]:
return "There is no user logged in."
credentials = config["configurable"]["_credentials"]
user = credentials.get("user")
if not user:
return "There is no user logged in."
user_email = user.get("email")
vector_store = await get_vector_store()
if not vector_store:
return "There is no vector store."
retriever = FGARetriever(
retriever=vector_store.as_retriever(),
build_query=lambda doc: ClientBatchCheckItem(
user=f"user:{user_email}",
object=f"doc:{doc.metadata.get('document_id')}",
relation="can_view",
),
)
documents = retriever.invoke(question)
return "\n\n".join([document.page_content for document in documents])
get_context_docs = StructuredTool(
name="get_context_docs",
description="Use the tool when user asks for documents or projects or anything that is stored in the knowledge base",
args_schema=GetContextDocsSchema,
coroutine=get_context_docs_fn,
)
backend/app/api/routes/chat.py file with the following code to pass the user credentials to your agent:backend/app/api/routes/chat.py
# ...
from app.core.auth import auth_client
# ...
@agent_router.api_route(
"/{full_path:path}", methods=["GET", "POST", "DELETE", "PATCH", "PUT", "OPTIONS"]
)
async def api_route(
request: Request, full_path: str, auth_session=Depends(auth_client.require_session)
):
try:
# ... existing code
# Prepare body
body = await request.body()
if request.method in ("POST", "PUT", "PATCH") and body:
content = await request.json()
content["config"] = {
"configurable": {
"_credentials": {
"user": auth_session.get("user"),
}
}
}
body = json.dumps(content).encode("utf-8")
# ... existing code
backend/app/agents/assistant0.py file with the following code to add the tool to your agent:backend/app/agents/assistant0.py
# ...
from app.agents.tools.context_docs import get_context_docs
tools = [get_context_docs]
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4.1-mini")
# ... existing code
agent = create_react_agent(
llm,
tools=ToolNode(tools, handle_tool_errors=False),
prompt=get_prompt(),
)
Test your application
To test the application, start the database, FastAPI backend, LangGraph server, and the frontend:
- Start the FastAPI backend:
cd backend
# start the postgres database
docker compose up -d
# start the FastAPI backend
source .venv/bin/activate
fastapi dev app/main.py
- In another terminal, start the LangGraph server:
cd backend
source .venv/bin/activate
uv pip install -U langgraph-api
langgraph dev --port 54367 --allow-blocking
This will open the LangGraph Studio in a new tab. You can close it as we won’t
require it for testing the application.
- In another terminal, start the frontend:
cd frontend
cp .env.example .env # Copy the `.env.example` file to `.env`.
npm install
npm run dev
http://localhost:5173 in your browser.
Upload a document from the documents tab and ask your AI agent a question about the document. You should get a response with the relevant information.Go to an incognito window, log in as a different user, and ask it the same question. You should not get a response.Share the document from the documents page to the second user and try again. You should see the information now.That’s it! You successfully integrated RAG protected by Auth0 FGA into your project.Explore the example app on GitHub.Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you:
Create an Auth0 FGA account
Install dependencies
As a first step, let’s get all dependencies installed:Create a new Node.js project
npm init -y
npm install langchain@0.3 @langchain/langgraph@0.2 @auth0/ai-langchain@3 dotenv@16
Set up an FGA Store
In the Auth0 FGA dashboard:Navigate to Settings. In the Authorized Clients section, click +
Create Client.
Give your client a name and mark all the client permissions that are
required for your use case. For the quickstart, you’ll only need Read and
query.
.env.local file with the following content to the root directory of the project. Click Continue to see the FGA_API_URL and FGA_API_AUDIENCE.The confirmation dialog will provide you with all the information that you need for your environment file.# You can use any provider of your choice supported by Vercel AI
OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
# Auth0 FGA
FGA_STORE_ID=<your-fga-store-id>
FGA_CLIENT_ID=<your-fga-store-client-id>
FGA_CLIENT_SECRET=<your-fga-store-client-secret>
FGA_API_URL=https://api.xxx.fga.dev
FGA_API_AUDIENCE=https://api.xxx.fga.dev/
model
schema 1.1
type user
type doc
relations
define owner: [user]
define viewer: [user, user:*]
- User:
user:*
- Object: select doc and add
public-doc in the ID field
- Relation:
viewer
A tuple signifies a user’s relation to a given object. For example, the above tuple implies that all users can view the public-doc object.After configuring your FGA Store, let’s get back to our node.js project. There you’ll secure the RAG tool using Auth0 FGA and Auth0 AI SDK.Get the Assets
Create an assets folder and download the below files into the folder:Create helper functions
Create a LangGraph agent and other helper functions that are needed to load documents.The first helper will create an in-memory vector store using faiss and OpenAIEmbeddings. You can replace this module with your own store, as long as it follows the LangChain retriever specification.import fs from "node:fs/promises";
import { StructuredToolInterface } from "@langchain/core/tools";
import { createReactAgent } from "@langchain/langgraph/prebuilt";
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { Document } from "@langchain/core/documents";
export class RetrievalAgent {
private agent;
private constructor(agent) {
this.agent = agent;
}
// Create a retrieval agent with a retriever tool and a language model
static create(tools: StructuredToolInterface[]) {
// Create a retrieval agent that has access to the retrieval tool.
const retrievalAgent = createReactAgent({
llm: new ChatOpenAI({ temperature: 0, model: "gpt-4o-mini" }),
tools,
stateModifier: [
"Answer the user's question only based on context retrieved from provided tools.",
"Only use the information provided by the tools.",
"If you need more information, ask for it.",
].join(" "),
});
return new RetrievalAgent(retrievalAgent);
}
// Query the retrieval agent with a user question
async query(query: string) {
const { messages } = await this.agent.invoke({
messages: [
{
role: "user",
content: query,
},
],
});
return messages.at(-1)?.content;
}
}
async function readDoc(path: string) {
return await fs.readFile(path, "utf-8");
}
/* Reads documents from the assets folder and converts them to langChain Documents */
export async function readDocuments() {
const folderPath = "./assets";
const files = await fs.readdir(folderPath);
const documents: Document[] = [];
for (const file of files) {
documents.push(
new Document({
pageContent: await readDoc(`${folderPath}/${file}`),
metadata: { id: file.slice(0, file.lastIndexOf(".")) },
})
);
}
return documents;
}
Create a RAG Pipeline
Define a RAG tool that uses the FGARetriever to filter authorized data from an in-memory vector database.In the first step, we will define a new RAG tool. The agent calls the tool when needed.import "dotenv/config";
import { OpenAIEmbeddings } from "@langchain/openai";
import { MemoryVectorStore } from "langchain/vectorstores/memory";
import { FGARetriever } from "@auth0/ai-langchain/RAG";
import { readDocuments, RetrievalAgent } from "./helpers";
async function main() {
console.info(
"\n..:: LangGraph Agents Example: Agentic Retrieval with Auth0 FGA \n\n"
);
const user = "user1";
// 1. Read and load documents from the assets folder
const documents = await readDocuments();
// 2. Create an in-memory vector store from the documents for OpenAI models.
const vectorStore = await MemoryVectorStore.fromDocuments(
documents,
new OpenAIEmbeddings({ model: "text-embedding-3-small" })
);
// 3. Create a retriever that uses FGA to gate fetching documents on permissions.
const retriever = FGARetriever.create({
retriever: vectorStore.asRetriever(),
// FGA tuple to query for the user's permissions
buildQuery: (doc) => ({
user: `user:${user}`,
object: `doc:${doc.metadata.id}`,
relation: "viewer",
}),
});
// 4. Convert the retriever into a tool for an agent.
const fgaTool = retriever.asJoinedStringTool();
// 5. The agent will call the tool, rephrasing the original question and
// populating the "query" argument, until it can answer the user's question.
const retrievalAgent = RetrievalAgent.create([fgaTool]);
// 6. Query the retrieval agent with a prompt
const answer = await retrievalAgent.query("Show me forecast for ZEKO?");
console.info(answer);
}
main().catch(console.error);
Run the application
To run the application, add the below to package.json:"x-type": "module",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "npx tsx index.ts"
},
npm start, and the agent will respond that it cannot find the required information.The application can retrieve the information if you change the query to something available in the public document.Now, to access the private information, you’ll need to update your tuple list. Go back to the Okta FGA dashboard in the Tuple Management section and click + Add Tuple. Fill in the following information:
- User:
user:user1
- Object: select doc and add
private-doc in the ID field
- Relation:
viewer
Now, click Add Tuple and then run npm start again. This time, you should see a response containing the forecast information since you added a tuple that defines the viewer relation for user1 to the private-doc object.Explore the example app on GitHub.Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you:
Create an Auth0 FGA account
Install dependencies
Please use Python version >=3.11 and <4.0.As a first step, let’s create a virtual environment and install the dependencies:# Create a virtual env
python -m venv venv
# Activate the virtual env
source ./venv/bin/activate
# Install dependencies
pip install langgraph langchain-openai python-dotenv faiss-cpu langchain-community auth0-ai-langchain langgraph-prebuilt
Set up an FGA Store
In the Auth0 FGA dashboard:Navigate to Settings. In the Authorized Clients section, click +
Create Client.
Give your client a name and mark all the client permissions that are
required for your use case. For the quickstart, you’ll only need Read and
query.
.env.local file with the following content to the root directory of the project. Click Continue to see the FGA_API_URL and FGA_API_AUDIENCE.The confirmation dialog will provide you with all the information that you need for your environment file.# You can use any provider of your choice supported by Vercel AI
OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
# Auth0 FGA
FGA_STORE_ID=<your-fga-store-id>
FGA_CLIENT_ID=<your-fga-store-client-id>
FGA_CLIENT_SECRET=<your-fga-store-client-secret>
FGA_API_URL=https://api.xxx.fga.dev
FGA_API_AUDIENCE=https://api.xxx.fga.dev/
model
schema 1.1
type user
type doc
relations
define owner: [user]
define viewer: [user, user:*]
- User:
user:*
- Object: select doc and add
public-doc in the ID field
- Relation:
viewer
A tuple signifies a user’s relation to a given object. For example, the above tuple implies that all users can view the public-doc object.After all this configuration, let’s get back to our node.js project. There you’ll secure the RAG tool using Auth0 FGA and Auth0 AI SDK.Get the assets
Create an assets folder and download the below files into the folder:Create helper functions
Create a LangGraph agent and other helper functions that are needed to load documents.The first helper will create an in-memory vector store using faiss and OpenAIEmbeddings. You can replace this module with your own store, as long as it follows the LangChain retriever specification.import faiss
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_community.docstore import InMemoryDocstore
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
class MemoryStore:
def __init__(self, store):
self.store = store
@classmethod
def from_documents(cls, documents):
embedding_model = OpenAIEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-ada-002")
index = faiss.IndexFlatL2(1536)
docstore = InMemoryDocstore({})
index_to_docstore_id = {}
vector_store = FAISS(embedding_model, index, docstore, index_to_docstore_id)
vector_store.add_documents(documents)
return cls(vector_store)
def as_retriever(self):
return self.store.as_retriever()
helpers/read_documents.py
import os
from langchain_core.documents import Document
def read_documents():
current_dir = os.path.dirname(__file__)
public_doc_path = os.path.join(current_dir, "../docs/public-doc.md")
private_doc_path = os.path.join(current_dir, "../docs/private-doc.md")
with open(public_doc_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as file:
public_doc_content = file.read()
with open(private_doc_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as file:
private_doc_content = file.read()
documents = [
Document(
page_content=public_doc_content,
metadata={"id": "public-doc", "access": "public"},
),
Document(
page_content=private_doc_content,
metadata={"id": "private-doc", "access": "private"},
),
]
return documents
Create a RAG Pipeline
Define a RAG tool that uses the FGARetriever to filter authorized data from an in-memory vector database.In the first step, we will define a new RAG tool. The agent will call up the tool when needed.@tool
def agent_retrieve_context_tool(query: str):
"""Call to get information about a company, e.g., What is the financial outlook for ZEKO?"""
documents = read_documents()
vector_store = MemoryStore.from_documents(documents)
user_id = "admin"
retriever = FGARetriever(
retriever=vector_store.as_retriever(),
build_query=lambda doc: ClientBatchCheckItem(
user=f"user:{user_id}",
object=f"doc:{doc.metadata.get('id')}",
relation="viewer",
),
)
relevant_docs = retriever.invoke(query)
if len(relevant_docs) > 0:
return "\n\n".join([doc.page_content for doc in relevant_docs])
return "I don't have any information on that."
tools = [agent_retrieve_context_tool]
FGARetriever defined in the retrieve node is designed to abstract the base retriever from the FGA query logic. In this case, the build_query argument lets us specify how to query our FGA model by asking if the user is a viewer of the document.# ...
build_query=lambda doc: ClientBatchCheckItem(
user=f"user:{user_id}",
object=f"doc:{doc.metadata.get('id')}",
relation="viewer",
),
# ...
def agent_node(state: State):
"""
Generate the response from the agent.
"""
llm_response = llm.invoke(state["messages"])
return {"messages": [llm_response]}
def agent_should_continue(state: State):
"""
Determines whether the conversation should continue based on the user input.
"""
last_message = state["messages"][-1]
if last_message.tool_calls:
return "tools"
return END
def generate_response_node(state: State):
"""
Generate the response from the agent based on the result of the RAG tool.
"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="""You are an assistant for question-answering tasks. Use the following pieces of retrieved-context to answer the question. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know. Use three sentences maximum and keep the answer concise. Question: {question}. Context: {context}. Answer:""",
input_variables=["question", "context"],
)
question = state["messages"][0].content
context = state["messages"][-1].content
chain = prompt | llm
llm_response = chain.invoke(
{"question": question, "context": context}, prompt=prompt
)
return {"messages": [llm_response]}
# ...
# Create the OpenAI chat tool
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini").bind_tools(tools)
# Build the graph
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
tool_node = ToolNode(tools)
# Define the nodes
graph_builder.add_node("agent", agent_node)
graph_builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
graph_builder.add_node("generate_response", generate_response_node)
# Run the graph
result = graph.invoke(
{"messages": [("human", "What is the financial outlook for ZEKO?")]}
)
print(result["messages"][-1].content)
Run the application
To run the application, simply run the Python script as follows:The application can retrieve the information if you change the query to something available in the public document. Now, to access the private information, you’ll need to update your tuple list. Go back to the Auth0 FGA dashboard in the Tuple Management section and click + Add Tuple. Fill in the following information:
- User:
user:user1
- Object: select doc and add
private-doc in the ID field
- Relation:
viewer
Now, click Add Tuple and then run npm start again. This time, you should see a response containing the forecast information since you added a tuple that defines the viewer relation for user1 to the private-doc object.Next.js
FastAPI
Node.js
Python